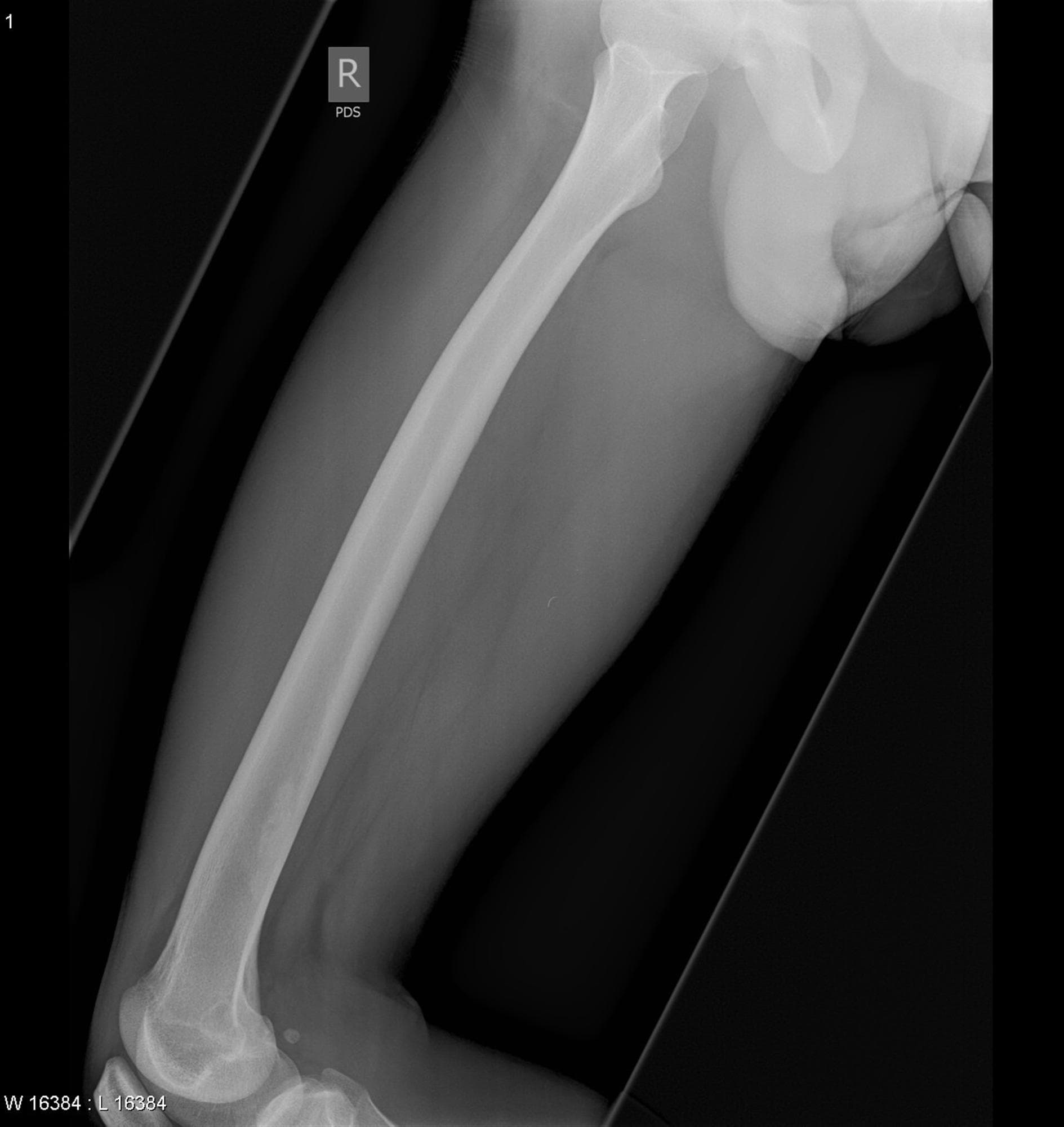
Femur Projections
Patient Preparation
- Explain the procedure to the patient.
- Remove clothing and metallic objects from the area of interest.
- Position the patient comfortably and immobilize the limb to prevent motion.
- Use lead shielding as appropriate.
- SID: Standard 100–120 cm (40–48 inches), adjust for horizontal beam lateral as needed.
BASIC PROJECTIONS
1. Anteroposterior (AP) Projection — Femur
Positioning:
- Patient supine on the table.
- Entire leg extended.
- For proximal femur, rotate the leg medially 10–15° to place femoral neck parallel to the IR.
- Center the femur to the IR.
- Include both hip and knee joints if possible.
Central Ray (CR):
- Perpendicular to the IR.
- Directed to the midpoint of the femur.
SID:
- 100–120 cm (40–48 inches).
Collimation:
- Include entire femur, hip, and knee depending on region imaged.
Evaluation Criteria:
- Entire femur visualized.
- Proper alignment with no rotation.
- Sharp bony detail from proximal to distal femur.
2. Lateral (Mediolateral) Projection — Femur
Positioning:
- Distal femur: Patient lies on affected side, opposite leg behind for support, knee flexed slightly.
- Proximal femur: Supine, affected limb laterally rotated, unaffected limb flexed for comfort.
- Center femur to the IR.
Central Ray (CR):
- Perpendicular to IR.
- Directed to midpoint of the femur.
SID:
- 100–120 cm (40–48 inches).
Collimation:
- Include entire femur or specific region.
Evaluation Criteria:
- Superimposition of femoral condyles (distal lateral).
- Femoral neck in profile (proximal lateral).
- Clear bony trabecular detail.
OTHER PROJECTIONS
3. Horizontal Beam Lateral — Femur (Trauma)
Indication:
- Used when patient cannot rotate or elevate leg (e.g., trauma, suspected fracture).
Positioning:
- Patient supine or sitting upright on stretcher.
- IR placed vertically on lateral side of femur.
- Affected limb in true lateral position.
- Opposite leg supported out of field.
Central Ray (CR):
- Horizontal and perpendicular to femur.
- Directed to midpoint of femur.
SID:
- Adjust to 100–120 cm (40–48 inches) as patient and stretcher allow.
Collimation:
- Include femur from hip to knee as much as patient tolerance allows.
Evaluation Criteria:
- True lateral view of femur.
- Superimposed femoral condyles (distal) or proper proximal alignment.
- Sharp bony detail without rotation.
Image Evaluation Checklist
- Entire femur included or as much as clinically possible.
- Correct exposure and contrast.
- No motion (except if unavoidable in trauma).
- Proper anatomical markers visible.
- Correct SID maintained for image quality.
Common Pathologies Demonstrated
- Femoral fractures (proximal, midshaft, distal).
- Postoperative alignment after fixation.
- Tumors or bone lesions.
- Hip or knee joint abnormalities (when included in image).