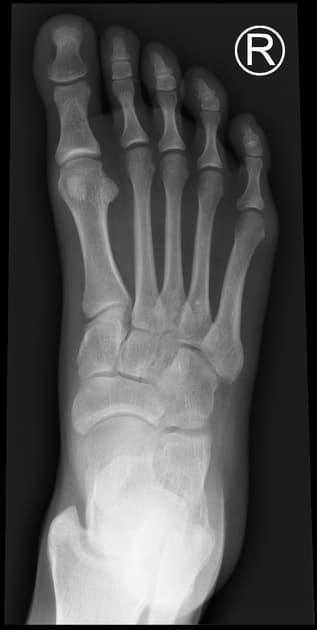
Foot Projections
Patient Preparation
- Explain the procedure to the patient.
- Remove shoes, socks, and any metallic objects from the area of interest.
- Ensure the foot is clean and comfortable.
- Use lead shielding as appropriate.
BASIC PROJECTIONS
1. Dorsoplantar (AP) Projection — Foot
Positioning:
- Patient seated or supine with the plantar surface of the foot resting flat on the image receptor (IR).
- Ensure the foot is centered and aligned with the long axis of the IR.
Central Ray (CR):
- Directed 10° posteriorly (toward the heel).
- Enters at the base of the third metatarsal.
Collimation:
- Include the entire foot from toes to the heel.
Evaluation Criteria:
- Equal spacing between the second to fifth metatarsals.
- Overlap between the bases of the second to fifth metatarsals.
- Visualization of phalanges, metatarsals, tarsals, and intertarsal joints.
2. AP Medial Oblique Projection — Foot
Positioning:
- Patient seated or supine.
- Knee flexed and plantar surface of foot resting on IR.
- Rotate the entire leg and foot medially by 30–40° (so plantar surface forms this angle with IR).
Central Ray (CR):
- Perpendicular to IR.
- Enters at the base of the third metatarsal.
Collimation:
- Include from toes to heel.
Evaluation Criteria:
- Open cuboid and lateral cuneiform joint spaces.
- Sinus tarsi clearly visualized.
- Bases of the first and second metatarsals overlapped.
- Bases of third to fifth metatarsals free of superimposition.
OTHER PROJECTIONS
3. Lateral Projection — Foot (Mediolateral)
Positioning:
- Patient lies on affected side.
- Opposite leg placed behind the affected leg.
- Foot dorsiflexed to form a right angle (90°) with the leg.
- Plantar surface perpendicular to IR.
Central Ray (CR):
- Perpendicular to IR.
- Enters at the base of the third metatarsal.
Collimation:
- Include entire foot and about 2.5 cm (1 inch) of distal tibia/fibula.
Evaluation Criteria:
- Superimposed metatarsal heads.
- Fibula overlapping the posterior portion of the tibia.
- Tibiotalar joint visualized.
- Clear soft tissue detail.
4. Weight-Bearing AP Projection — Foot (Bilateral or Single)
Positioning:
- Patient standing erect on IR.
- Feet centered and parallel, weight equally distributed on both feet.
- For bilateral projection, place IR under both feet.
Central Ray (CR):
- Angled 10–15° posteriorly toward the heel.
- Enters at the level of the base of the third metatarsal (for single) or midway between both feet (for bilateral).
Collimation:
- Include both feet from toes to heels (for bilateral).
Evaluation Criteria:
- Open tarsometatarsal and intermetatarsal joint spaces.
- Comparison of arches and alignment.
- Weight-bearing relationship between bones.
5. Weight-Bearing Lateral Projection — Foot
Positioning:
- Patient standing erect with one foot on IR.
- Opposite foot placed slightly backward for support.
- Weight evenly distributed on the foot being imaged.
- Foot perpendicular to IR.
Central Ray (CR):
- Horizontal beam directed to the level of the base of the third metatarsal.
Collimation:
- Include entire foot and distal tibia/fibula.
Evaluation Criteria:
- Visualization of longitudinal arch under load.
- Superimposed metatarsal heads.
- Proper soft tissue and bony detail.
- Assessment of foot alignment and arch height.
Image Evaluation Checklist
- Correct exposure and contrast.
- All phalanges, metatarsals, and tarsal bones visible.
- Sharp trabecular and cortical bone detail.
- Proper centering and anatomical markers used.
Common Pathologies Demonstrated
- Fractures of metatarsals, phalanges, or tarsals.
- Flatfoot (pes planus) or high arch (pes cavus).
- Osteoarthritis and bone alignment issues.
- Weight-bearing deformities.
- Soft tissue abnormalities.