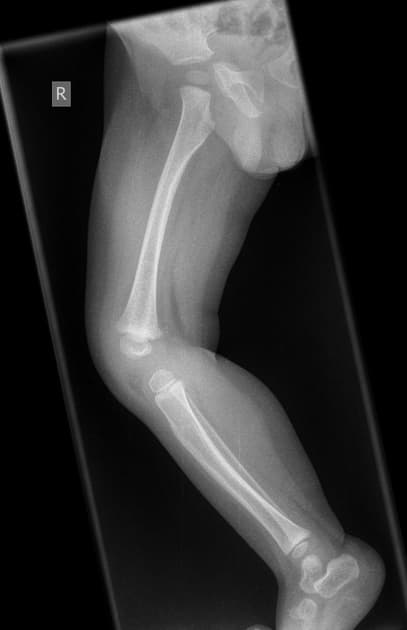
Lower Limb (Pediatric) Projections
Patient Preparation
- Explain the procedure gently to both the child and guardian.
- Remove any clothing, shoes, or metallic objects from the area of interest.
- Immobilization aids or parental assistance may be used for comfort and to prevent motion.
- Use appropriate pediatric exposure settings and lead shielding.
BASIC PROJECTIONS
1. Anteroposterior (AP) Projection — Lower Limb
Positioning:
- Infant or child supine on the table.
- Both lower limbs extended.
- Feet dorsiflexed so that the plantar surfaces are vertical if possible.
- Center both limbs to the midline of the image receptor (IR).
Central Ray (CR):
- Perpendicular to the IR.
- Directed to the midpoint of the lower limbs.
Collimation:
- Include both hip and ankle joints.
Evaluation Criteria:
- Entire lower limb visualized from hip to ankle.
- No rotation — femoral condyles and tibial plateaus symmetric.
- Both joints (hip and ankle) included on the same image when possible.
2. Lateral Projection — Lower Limb (Mediolateral)
Positioning:
- Child lies on affected side.
- Opposite leg positioned behind for support.
- Slight flexion of the knee for stability.
- Ensure true lateral alignment — femoral condyles superimposed.
Central Ray (CR):
- Perpendicular to the IR.
- Directed to the midpoint of the lower limb.
Collimation:
- Include both knee and ankle joints.
Evaluation Criteria:
- Entire tibia and fibula visualized.
- Superimposed femoral condyles.
- Knee and ankle joints clearly demonstrated.
OTHER PROJECTIONS
3. Congenital Clubfoot (Talipes Equinovarus) — AP and Mediolateral
Positioning:
- Infant or child supine for AP view or on the affected side for lateral (mediolateral) view.
- Foot placed in its natural deformity — do not force correction.
- Center the foot or ankle to the IR.
- Use both AP (dorsoplantar) and mediolateral positioning as appropriate.
Central Ray (CR):
- Perpendicular to the IR.
- AP: Directed midway between the malleoli.
- Mediolateral: Directed to the midpoint of the foot.
Collimation:
- Include entire foot, ankle, and distal tibia/fibula.
Evaluation Criteria:
- Visualization of talus, calcaneus, and midfoot alignment.
- Foot anatomy shown without distortion.
- Both AP and mediolateral views demonstrate the congenital deformity.
Image Evaluation Checklist
- Entire lower limb or foot visualized as required.
- Correct exposure for pediatric anatomy.
- No motion or blurring.
- Anatomical markers correctly placed.
Common Pathologies Demonstrated
- Congenital clubfoot (talipes equinovarus).
- Leg length discrepancies.
- Fractures or developmental bone deformities.
- Growth plate (epiphyseal) abnormalities.